
ESG reports are often accused of lacking transparency, with data that is difficult to verify. This can lead to allegations of ‘greenwashing’, where companies embellish their environmental or social impact to improve their image with investors and consumers.
In a world where sustainability and transparency have become major concerns for companies, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) is now at the heart of modern business strategies. Companies are increasingly being held accountable for their environmental, social and governance practices, and stakeholders are demanding comprehensive and reliable ESG reports. However, traditional ESG reporting methods, which are often manual and error-prone, are no longer sufficient to meet growing expectations for transparency and accuracy.
This is where Web 3.0 comes in. This new iteration of the internet, powered by decentralised technologies such as blockchain, promises to transform ESG reporting by offering solutions that improve not only accuracy and transparency, but also the reliability of data. This article explores how blockchain, a key Web 3.0 technology, is revolutionising ESG reporting by solving some of the most pressing challenges facing companies today.
Buckle up, let's discover the future of ESG reporting !
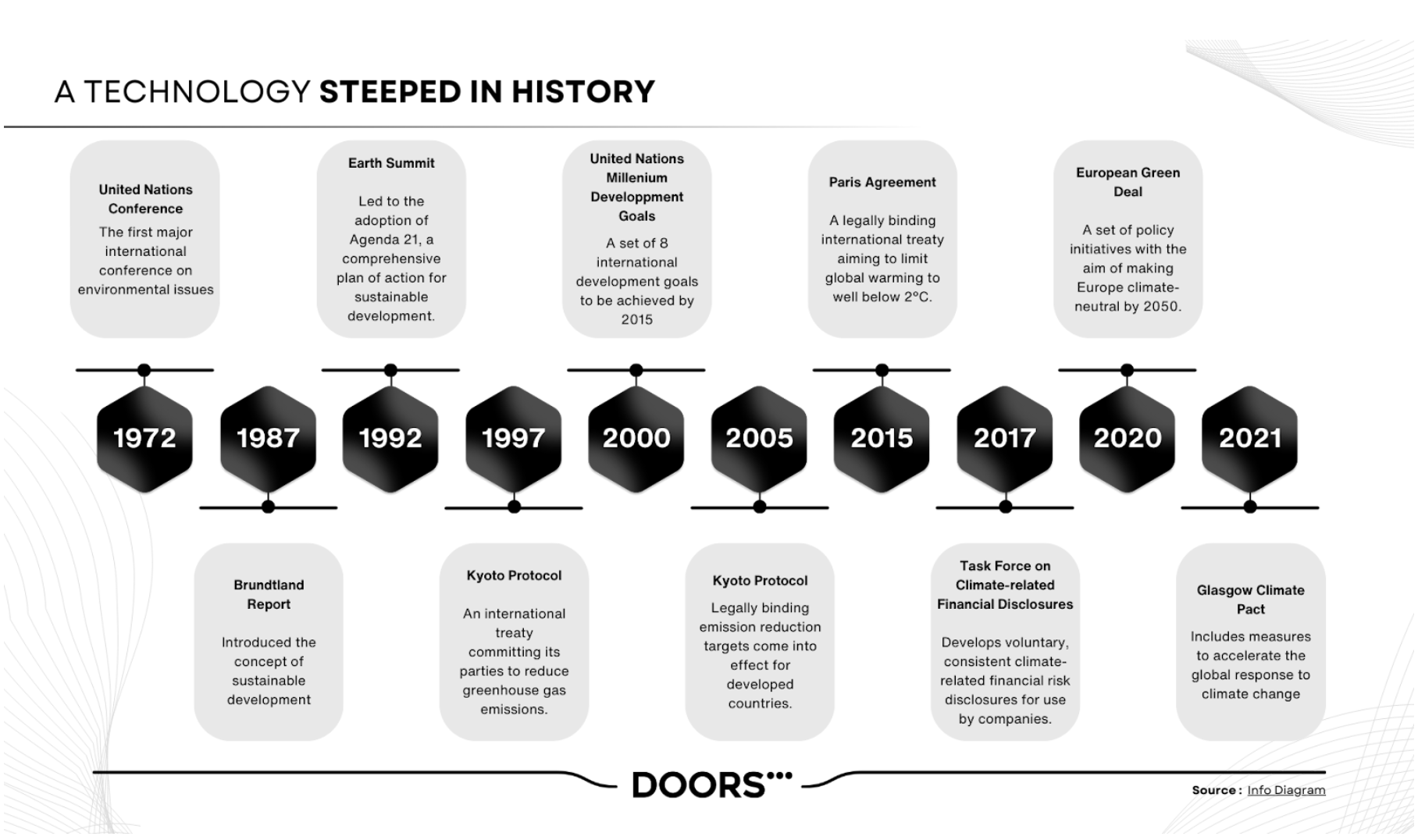
1 - Current Challenges of ESG Reporting
Traditional ESG reporting relies heavily on manual processes and data collection chains that are often complex and fragmented. This creates several major challenges:
1.1 - Data Collection and Authentication
Companies often need to gather data from multiple sources, both internal and external. This can be a time-consuming and error-prone process, particularly with regard to the authenticity of data provided by third parties, such as suppliers. Verifying this data to ensure its accuracy and reliability is a major challenge.
1.2 - Lack of Transparency
ESG reports are often accused of lacking transparency, with data that is difficult to verify. This can lead to allegations of ‘greenwashing’, where companies embellish their environmental or social impact to improve their image with investors and consumers.
1.3 - Inconsistent reporting
The absence of universal standards for ESG reporting leads to inconsistencies in the way data is collected, reported and interpreted. This makes it difficult for stakeholders to compare ESG performance between different companies.
2 - Introduction to Web 3.0 and Blockchain for greater transparency
Web 3.0 represents a major evolution of the Internet, marked by increased decentralisation, better protection of privacy, and the use of technologies such as blockchain. Unlike Web 2.0, where data is often centralised and controlled by large companies, Web 3.0 allows users and companies to own and control their data more transparently and securely.
Blockchain is at the heart of this transformation. It is a distributed ledger technology that allows data to be stored in an immutable and verifiable way, with no single entity having exclusive control over that data. This makes it particularly useful for ESG reporting, where data transparency and verifiability are crucial.

3 - How are blockchain and smart contracts improving ESG reporting?
Blockchain brings several key advantages that can solve the challenges of ESG reporting.
1. Data traceability and transparency: with blockchain, every transaction or piece of data added to the chain is time-stamped and immutable, meaning it cannot be modified or deleted. This makes it possible to track every stage of the ESG data collection process, ensuring that the information reported is accurate and verifiable. For example, a company can use blockchain to trace the origin of its raw materials and ensure that they come from sustainable sources.
2. Automation using smart contracts: smart contracts are autonomous programs that run automatically when predefined conditions are met. In the context of ESG reporting, they can be used to automate data collection, verification and reporting. For example, a smart contract could automatically flag up a breach of environmental standards if a plant exceeds a certain emissions threshold, and trigger an alert or corrective action.
3. Reduced risk of greenwashing: Thanks to the increased transparency and verifiability of data, blockchain reduces the risk of greenwashing. Companies can no longer easily manipulate or conceal information, as every piece of data is accessible to all stakeholders and cannot be altered once it has been entered into the blockchain.
4. Concrete examples of applications: Several pioneering projects demonstrate how blockchain is being used to improve ESG reporting. For example, initiatives in the supply chain sector are using blockchain to track products transparently, ensuring that the information reported on the sustainability and origin of products is accurate. Similarly, carbon credit management projects use blockchain to verify and track emissions reductions, ensuring the credibility of credits traded on carbon markets.
4 - Competitive advantages for companies adopting Web 3.0
The adoption of blockchain in ESG reporting has significant competitive advantages for companies. Not only can it improve their compliance with increasingly stringent regulations, but it can also boost investor and consumer confidence in their ESG practices. Companies that adopt these technologies early can position themselves as leaders in transparency and sustainability, attracting ethically minded investment and customers.
In addition, reducing the risks associated with greenwashing and regulatory non-compliance can help companies avoid potential sanctions and protect their reputation in the long term. By automating processes through smart contracts, they can also achieve operational efficiencies, reducing the costs associated with collecting and verifying ESG data.
Conclusion
Web 3.0, with blockchain at its heart, offers an unprecedented opportunity to revolutionise ESG reporting. By addressing today's challenges of data collection, transparency and verifiability, blockchain is enabling companies to provide more reliable and transparent ESG reports, boosting stakeholder confidence. As sustainability expectations continue to rise, companies that embrace Web 3.0 will be better prepared to meet future demands and position themselves as leaders in the new sustainable economy.
.png?width=150&height=75&name=Design%20sans%20titre%20(7).png)



